I am sure most of us, in one way or the other have experienced data inconsistency issues in a software system. For instance, while operating an ATM machine for withdrawing money, often people encounter failed transactions due to various reasons. The ATM machine might not dispense the currency, although may proceed to show balance deduction in the accounts. When customers report the failure in the system, the bank usually responds saying that it shall take 60 mins to 24 hours to resolve the erroneous transaction record. This is a typical case of data inconsistency wherein the ATM and the bank server are out of sync for a brief period.
Let us take another case of bill payment through mobile phone apps. The user initiates the payment, the app securely connects to the bank interface, payment is processed and is being handed over to the merchant interface to confirm the payment. Let us say the merchant website is unavailable at this moment. Now, the transaction remains incomplete for a brief period until the app servers sync up with the merchant interface.
Notice, in both the above cases the data inconsistencies are due to certain portions of the system being unavailable, services not responding, network induced errors etc., and these factors are very common in large distributed software systems. Though the system eventually over a period establishes consistency, a seamless and hassle-free end-user experience is not a certainty.
Microservices style of building software architecture adopts a distributed approach whereby each service/function of a software is highly independent, has a specific business boundary or a defined context, may or may not know of the existence of other services, is capable of managing its own data, can use different storing mechanisms and is possibly authored in different programming languages, and maintained by separate teams.
Microservices architecture uses a decentralizing approach and is much inspired by the nature. Microservices have become a popular choice for building huge enterprise systems. With the advent of cloud, elastic computing and storage, and container tech and orchestration mechanisms, there is a huge surge in building applications using Microservices architectural style.
By now, you might have already figured out that owing to the strong advocacy of decentralized data approach of the microservices architecture, it induces eventual data consistency in the systems. However, it would not be prudent to think that the monolithic software architecture deals with these issues seamlessly. They have their own perils.
It is thus imperative that microservice developers take these issues into consideration and be aware of the challenges that can creep in the eventual data consistency. The below listed techniques helps in managing the eventual consistency in Microservices.
Saga Pattern
Transactions that span multiple services are viewed as a saga/chain of simple atomic local transactions at each service level. Thus, a service completes and commits its transaction, notifies the next service in the chain with an event/message to trigger the next local transaction and so on and so forth. If one transaction in this chain fails, owing to any particular reason, it basically triggers an undo operation coming backward in the chain. It is thus imperative to address pattern failures while designing the architecture.
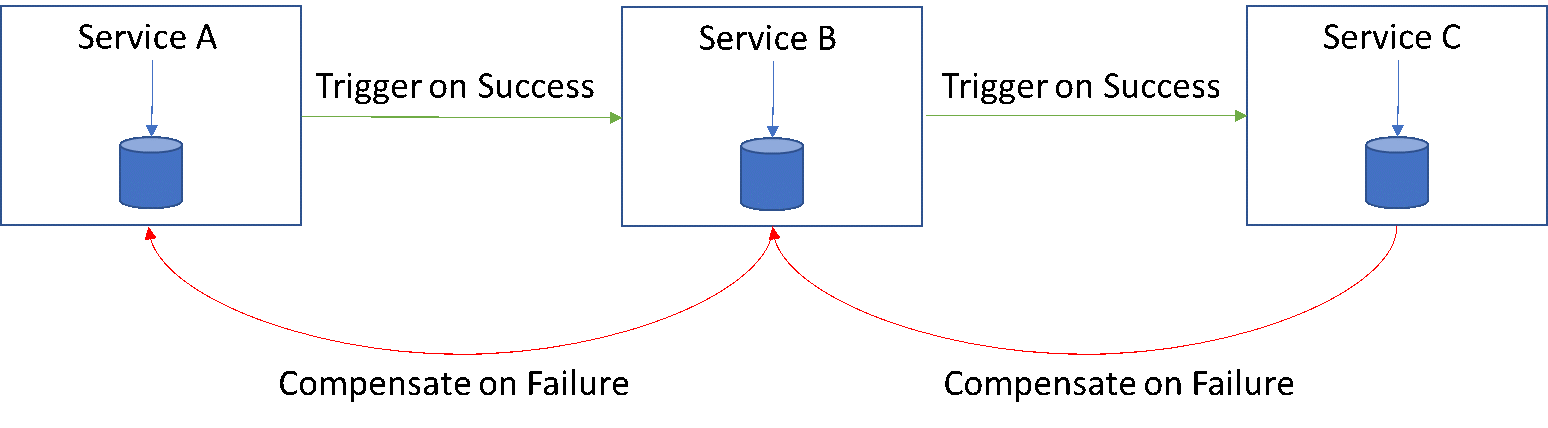
Saga pattern though addresses the eventual consistency issues, is more suitable for a smaller distributed architecture than large scale. The designers also need to consider that compensation calls/transactions can also fail. Thus, making it suitable for simpler and small distributed architecture.
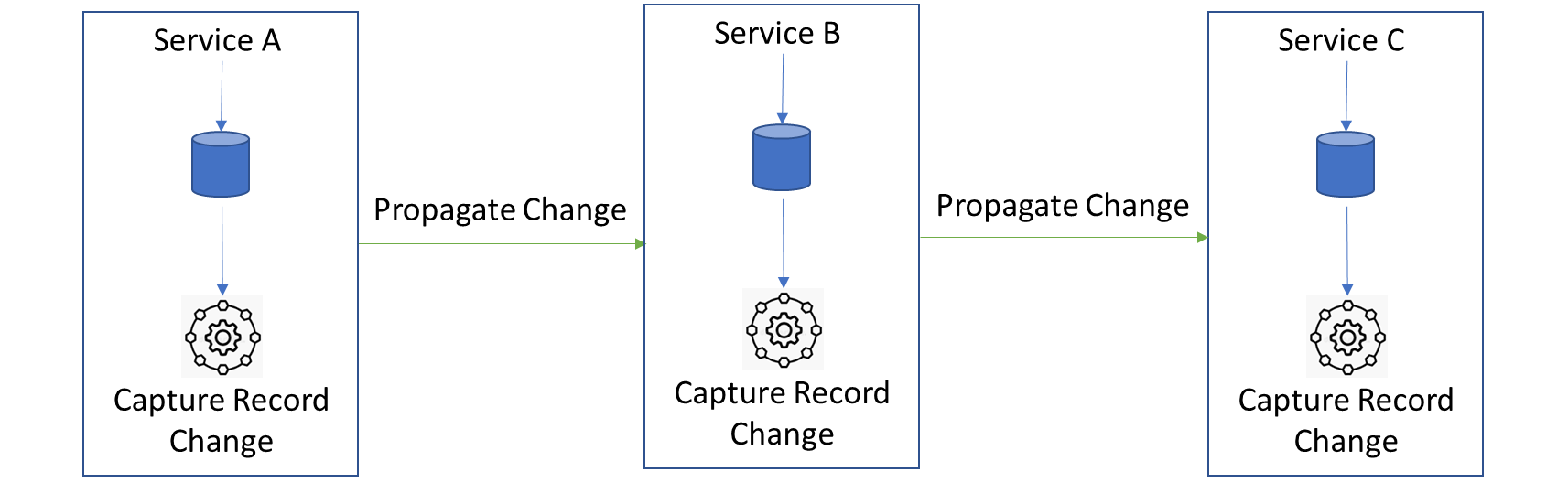
Change Data Capture (CDC)
CDC, although well rooted and practiced extensively in Data Warehousing, can well be adopted to Microservices design effectively to ensure that the transactions span services with consistency.
The basic principle remains same at the core. A service, after its local transaction commits itself to the local DB, triggers a separate process that creates a change capture record and propagates the change capture record to the next service. This service takes in the change capture record from the previous service, processes it, commits to its local DB and in a separate process within, creates its own new change capture record and propagates it to the next set of services.
Thus, this change capture record can be propagated through the distributed services until all services are in sync without any great stress on orchestration.
Ways to implement CDC in Microservices:
Using Database Transaction Logs: Many databases offer operational logs and transactional logs. By scanning the contents of these logs and interpreting the changes, one can identify the changes made to database. This can be the change capture record to be propagated to the next service.
Using Kafka Connect and Apache Kafka: The DB changes captured made in a service can be hooked into a Kafka connecter which effectively stems the changes to the various Kafka topics for the subscribers to consume and act.
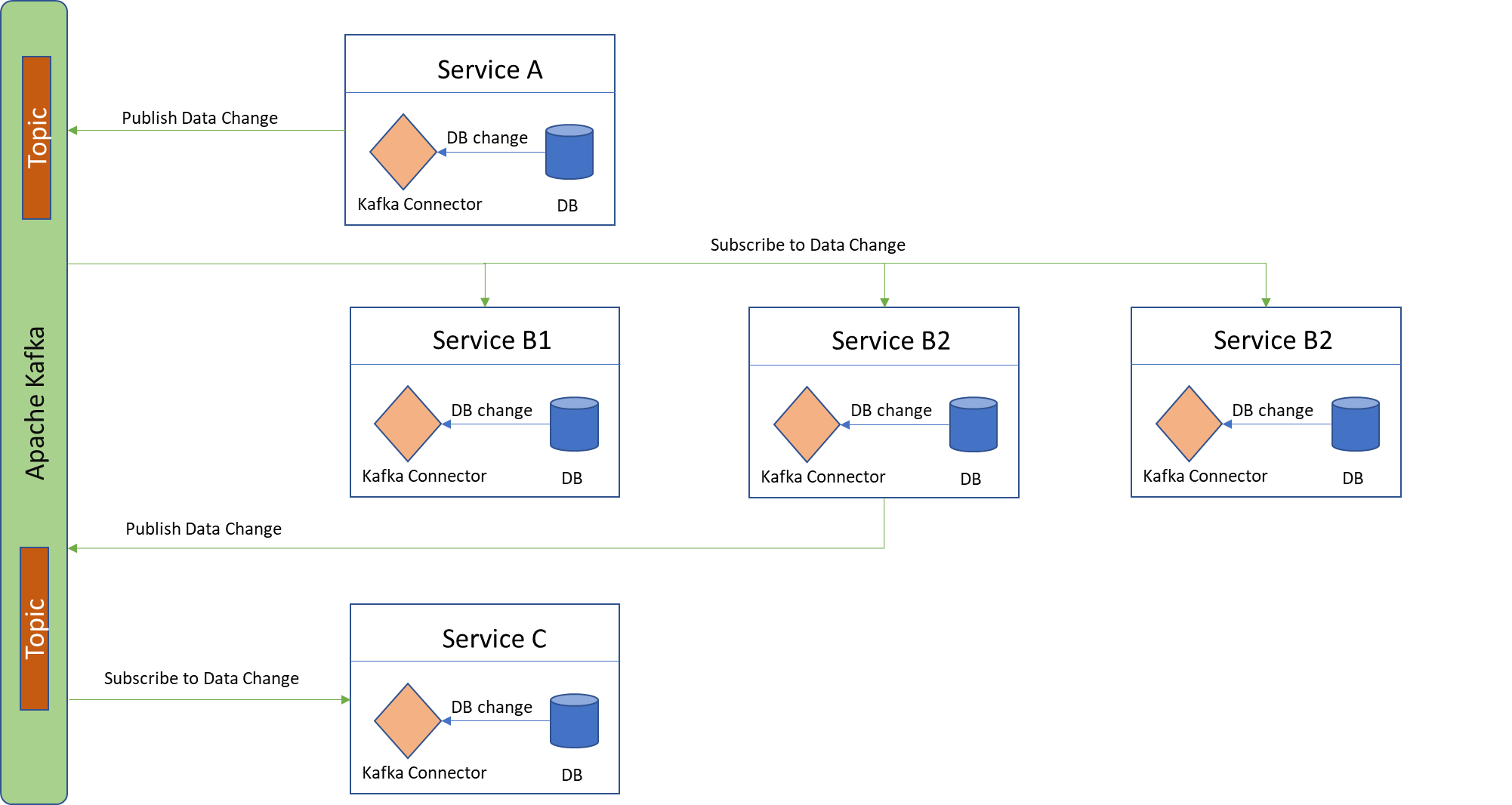
CDC in general is suitable for large distributed architecture styles, as it is not performance heavy and it can be easily enabled without wanting to have any extra changes to the schema. CDC inherently carries lower latency and enables downstream databases to quick tail the change. There is also a possibility to run stream processing on the change feed received by services.
However, the most important drawback designers feel in CDC is the inflexibility to change the schema of the services. This blocks the evolution of service DB schema to an extent. Changing schema in a service triggers change in all downstream services.
Besides these two ways, there are several other ways of achieving data sync through CDC which have been implemented by cloud infra providers.
Having seen two popular approaches to achieve data consistency and integration and their drawbacks, let us now consider a totally new perspective and paradigm to view the issue of data consistency... “Accepting the Inconsistency” - Not all software systems/parts of the system need the data to be synced and be consistent all the time. Let us rewind back to our example of money withdrawal through ATM. We all have accepted the data inconsistency here and wait for the system to become consistent over a period.
Many business systems are more tolerant of the data inconsistencies than usually believed. This is because, businesses stress and monetize more on service availability, leading us to the long-lasting debate on prizing BASE over ACID in many enterprise scale systems.
BASE is an acronym for Basically Available, Soft state and Eventual Consistency
ACID is an acronym for Atomicity, Consistent, Isolated and Durable
This is in line with the popular CAP theorem which states, that it is impossible for a distributed data store to simultaneously provide more than two out of the following three guarantees Consistency, Availability and Partition tolerance.
Thus, software systems always prize either BASE over ACID or vice-versa suiting there need and keep parts of the system consistent.
Feel free to drop your comments, feedback, queries on this article, I will try and answer each of those at my earliest convenience.
Relevant Blogs

Building the Stadium Marketplace: How LTTS’ SportsStore Turns Fan Engagement into a Scalable Revenue Engine

Building the Stadium Marketplace: How LTTS’ SportsStore Turns Fan Engagement into a Scalable Revenue Engine


